Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –
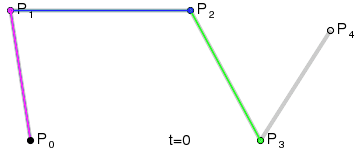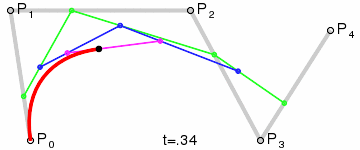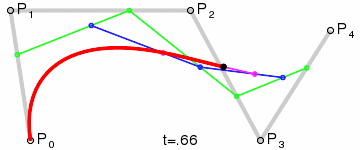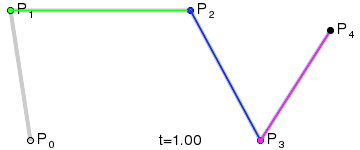
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that the discovery of Descartes' theorem in geometry came from a too-difficult mathematics problem posed to a princess?
- ... that mathematics professor Ari Nagel has fathered more than a hundred children?
- ... that Green Day's "Wake Me Up When September Ends" became closely associated with the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina?
- ... that mathematician Daniel Larsen was the youngest contributor to the New York Times crossword puzzle?
- ... that two members of the French parliament were killed when a delayed-action German bomb exploded in the town hall at Bapaume on 25 March 1917?
- ... that the music of math rock band Jyocho has been alternatively described as akin to "madness" or "contemplative and melancholy"?
- ... that Catechumen, a Christian first-person shooter, was funded only in the aftermath of the Columbine High School massacre?
- ... that Fairleigh Dickinson's upset victory over Purdue was the biggest upset in terms of point spread in NCAA tournament history, with Purdue being a 23+1⁄2-point favorite?
More did you know –

- ... that the Herschel graph is the smallest possible polyhedral graph that does not have a Hamiltonian cycle?
- ... that the Life without Death cellular automaton, a mathematical model of pattern formation, is a variant of Conway's Game of Life in which cells, once brought to life, never die?
- ... that one can list every positive rational number without repetition by breadth-first traversal of the Calkin–Wilf tree?
- ... that the Hadwiger conjecture implies that the external surface of any three-dimensional convex body can be illuminated by only eight light sources, but the best proven bound is that 16 lights are sufficient?
- ... that an equitable coloring of a graph, in which the numbers of vertices of each color are as nearly equal as possible, may require far more colors than a graph coloring without this constraint?
- ... that no matter how biased a coin one uses, flipping a coin to determine whether each edge is present or absent in a countably infinite graph will always produce the same graph, the Rado graph?
- ...that it is possible to stack identical dominoes off the edge of a table to create an arbitrarily large overhang?
Selected article –
 |
| The second Borel-Cantelli lemma implies that a chimpanzee like this one typing at random will almost surely produce the complete works of Shakespeare, given enough time. Image credit: User:Chris 73 |
The infinite monkey theorem states that a monkey hitting keys at random on a typewriter keyboard for an infinite amount of time will almost surely type or create a particular chosen text, such as the complete works of William Shakespeare. Note that "almost surely" in this context is a mathematical term with a specific meaning, and that the "monkey" is not an actual monkey; rather, it is a vivid metaphor for an abstract device that produces an unending, random sequence of letters.
The theorem graphically illustrates the perils of reasoning about infinity by imagining a vast but finite number. If every atom in the visible universe were a monkey producing a billion keystrokes a second from the Big Bang until today, it is still very unlikely that any monkey would get as far as "slings and arrows" in Hamlets most famous soliloquy. The infinite monkey theorem is straightforward to prove, even without appealing to more advanced results. ('Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus